Ancient civilizations have shaped our world today, leaving remarkable legacies that continue to intrigue us. These cultures have contributed signific
Ancient civilizations have shaped our world today, leaving remarkable legacies that continue to intrigue us. These cultures have contributed significantly to human history, from monumental architecture to complex societies. Here are ten fascinating facts about ancient civilizations that will broaden your understanding and appreciation of our collective past.
1. The Cradle of Civilizations: Mesopotamia
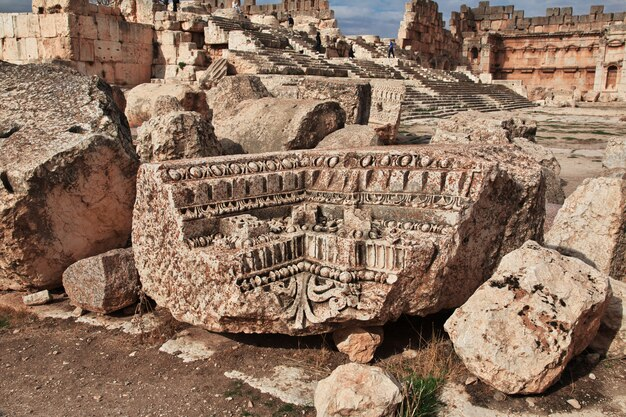

Often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in modern-day Iraq, is where some of the earliest urban centers emerged around 3500 BCE. The Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians thrived here, developing writing (cuneiform), mathematics, and laws. The Code of Hammurabi, one of the oldest deciphered writings of significant length, established principles of justice that resonate to this day.
2. The Ancient Civilizations of The Great Pyramids of Giza
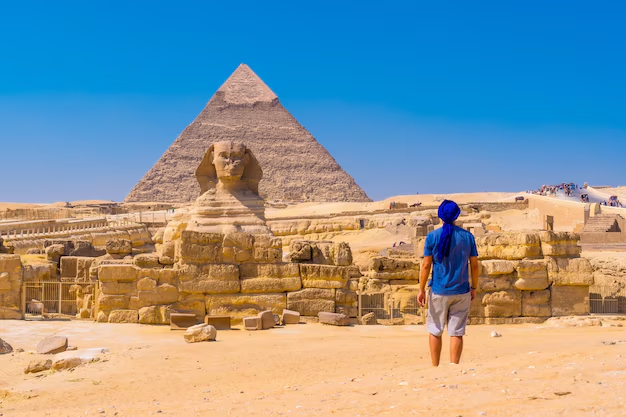

The Pyramids of Giza, built during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, remain one of the most iconic symbols of ancient engineering. Constructed over 4,500 years ago, the Great Pyramid of Khufu was the tallest man-made structure in the world for nearly 4,000 years. These pyramids were meticulously aligned with the stars and constructed with incredible precision, showcasing the Egyptians’ advanced understanding of mathematics and astronomy.
3. The Indus Valley Civilizations: A Mystery

Spanning present-day Pakistan and northwest India, the Indus Valley Civilization flourished around 2500 BCE. Despite its vast cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, much about this civilization remains a mystery. They had advanced urban planning, including grid layouts, sophisticated drainage systems, and standardized brick sizes. However, their script has yet to be deciphered, leaving scholars puzzled about their language and culture.
4. Ancient Greece: Birthplace of Democracy

Ancient Greece is often hailed as the birthplace of democracy, particularly in the city-state of Athens. In the 5th century BCE, Athenians developed a system where citizens could participate directly in decision-making. This revolutionary concept laid the groundwork for modern democratic systems. Furthermore, ancient Greece contributed significantly to philosophy, theater, and the arts, with figures like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle influencing countless generations.
5. The Roman Empire Civilizations: Engineering Marvels

At its height, the Roman Empire was one of the most powerful civilizations in history, spanning three continents. Renowned for its engineering feats, the Romans built extensive road networks, aqueducts, and monumental structures like the Colosseum. These innovations not only facilitated trade and communication but also demonstrated their advanced understanding of architecture and urban planning. The saying “All roads lead to Rome” stems from this vast network.
6. The Mayan Civilizations: Astronomy and Calendar

The Mayans, flourishing in Central America from around 2000 BCE to the Spanish conquest in the 16th century, are known for their extraordinary achievements in astronomy and mathematics. They developed a complex calendar system that was remarkably accurate, consisting of 365-day solar and 260-day ritual calendars. Their observations of celestial bodies were crucial for agriculture and religious practices, showcasing their deep connection to the cosmos.
7. The Silk Road: Cultural Exchange Civilizations

The Silk Road was not just a trade route; it was a vital artery for cultural exchange that connected the East and West. Spanning over 4,000 miles, this network facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, art, and religion between ancient civilizations such as China, Persia, and Rome. Innovations like paper, gunpowder, and the compass traveled along these routes, profoundly impacting societies across the globe.
8. The Ancient Egyptians Civilizations: Mummification and Afterlife Beliefs

The ancient Egyptians held a profound belief in the afterlife, which influenced their burial practices and architecture. Mummification was a meticulous process aimed at preserving the body for eternity, reflecting their views on immortality. Elaborate tombs, such as the Valley of the Kings, were filled with artifacts to assist the deceased in the afterlife. This reverence for the dead underscores the Egyptians’ unique spiritual worldview.
9. The Phoenicians: Masters of Trade and Navigation

The Phoenicians, an ancient civilization centered in modern-day Lebanon, were exceptional traders and navigators. They developed one of the first alphabets, which greatly influenced the Greek and Latin scripts. Their extensive maritime trade network spread across the Mediterranean, facilitating cultural exchange and the dissemination of goods such as purple dye, glass, and timber.
10. The Aksumite Empire: A Trading Power

The Aksumite Empire, located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, was a powerful trading civilization from around 100 CE to 940 CE. It played a crucial role in the trade between the Roman Empire and India, thanks to its strategic location. Aksum was also one of the first major empires to officially adopt Christianity, with King Ezana converting in the 4th century CE, highlighting its cultural significance.
Conclusion
Ancient civilizations have left an indelible mark on human history, influencing our cultures, beliefs, and technologies. From the democratic ideals of ancient Greece to the advanced engineering of the Romans and the astronomical knowledge of the Mayans, these societies have shaped the world we live in today. Exploring their fascinating achievements not only enriches our understanding of the past but also provides valuable insights into the future. Embrace the stories of these civilizations and appreciate the profound legacy they have left behind.
COMMENTS